Geoprocessing Model - Automating with Python
arcgispro
geospatial
map
esri
In this project we will learn three ways for storing and automating multiple-operation workflows. Workflow definition, storage, and automation facilitate and standardize geospatial solutions. These capabilities are especially useful for organizations that anticipate performing a workflow many times.
- Automating tasks — This feature allows we to walk the user through a series of predefined steps that can incorporate (or call) commands and geoprocessing tools, including model and script tools. It can serve as a best practices or a workflow tutorial—a documented series of instructions that call forth the correct commands or tools. And the tasks can be shared as part of a project, allowing users to share their knowledge.
- ModelBuilder™ — a geoprocessing environment that allows we to easily link one tool to another and run a set of operations one after another. ModelBuilder provides a helpful visual diagram of geoprocessing workflows and includes advanced capabilities such as looping and if-then scenarios.
- Automate with Python — We will write a command and use a custom script tool (created with Python) that performs multiple operations.
Study case scenario
We are employed by a nonprofit agency whose primary objective is to raise awareness of and develop solutions for international human rights violations. Taking advantage of the public information offered by the Armed Conflict Location and Event Data (ACLED) project, we are creating maps that convey the impact of political violence in developing countries. We will present our maps at an international human rights conference for eventual incorporation into an awareness campaign.
The Dataset
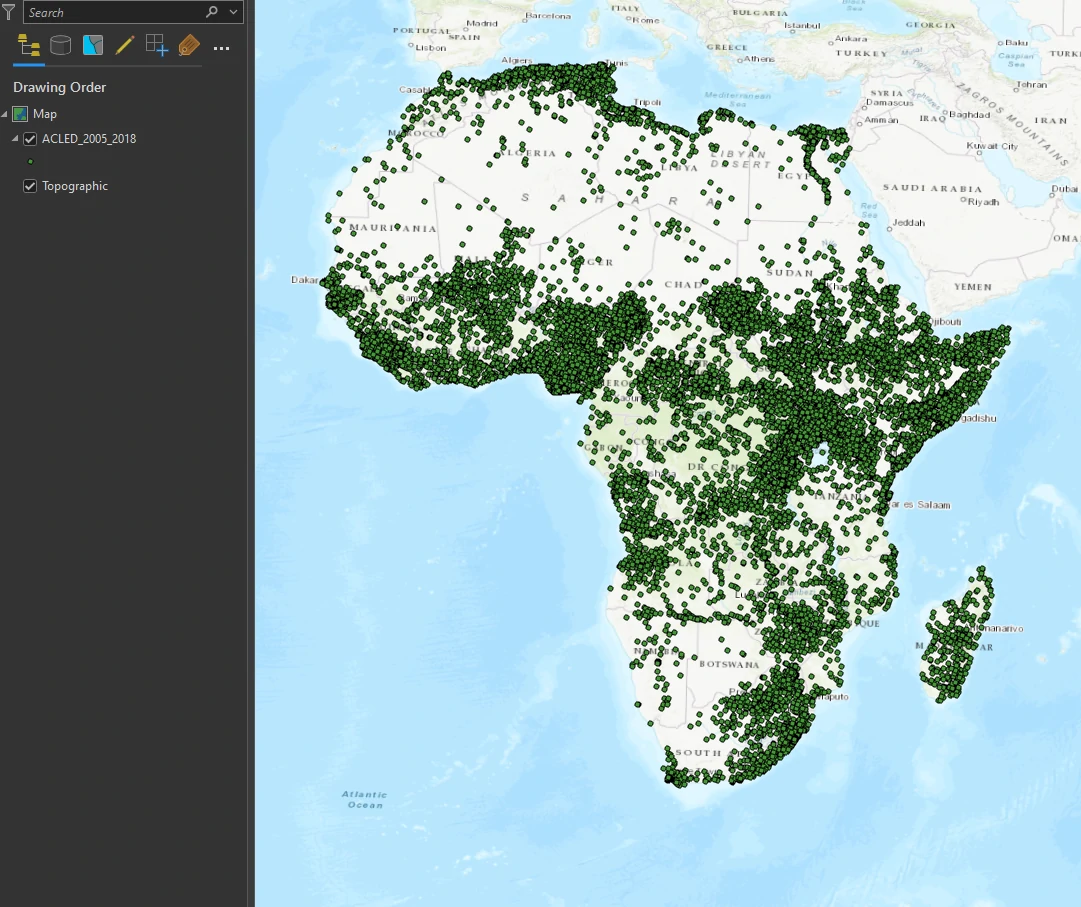
The ACLED dataset we are using provides information on political violence in developing countries. Attributes include dates of conflict events, key actors involved (such as military forces, protesters, rebel groups, civilians, and others), and event classification (such as riots and protests, battles, nonviolent activities by conflict actors, violence against civilians, and more). In this project, We will focus on African continent.
ACLED_2005_2018 — a point feature class that displays locations of armed conicts throughout Africa from 2005 to 2018 (Source: ACLED).
Automating with Python
We can also run geoprocessing tools, along with other functions, using Python. Python is a programming language that, in the GIS context, is used to script geoprocessing workflows and build custom geoprocessing tools.
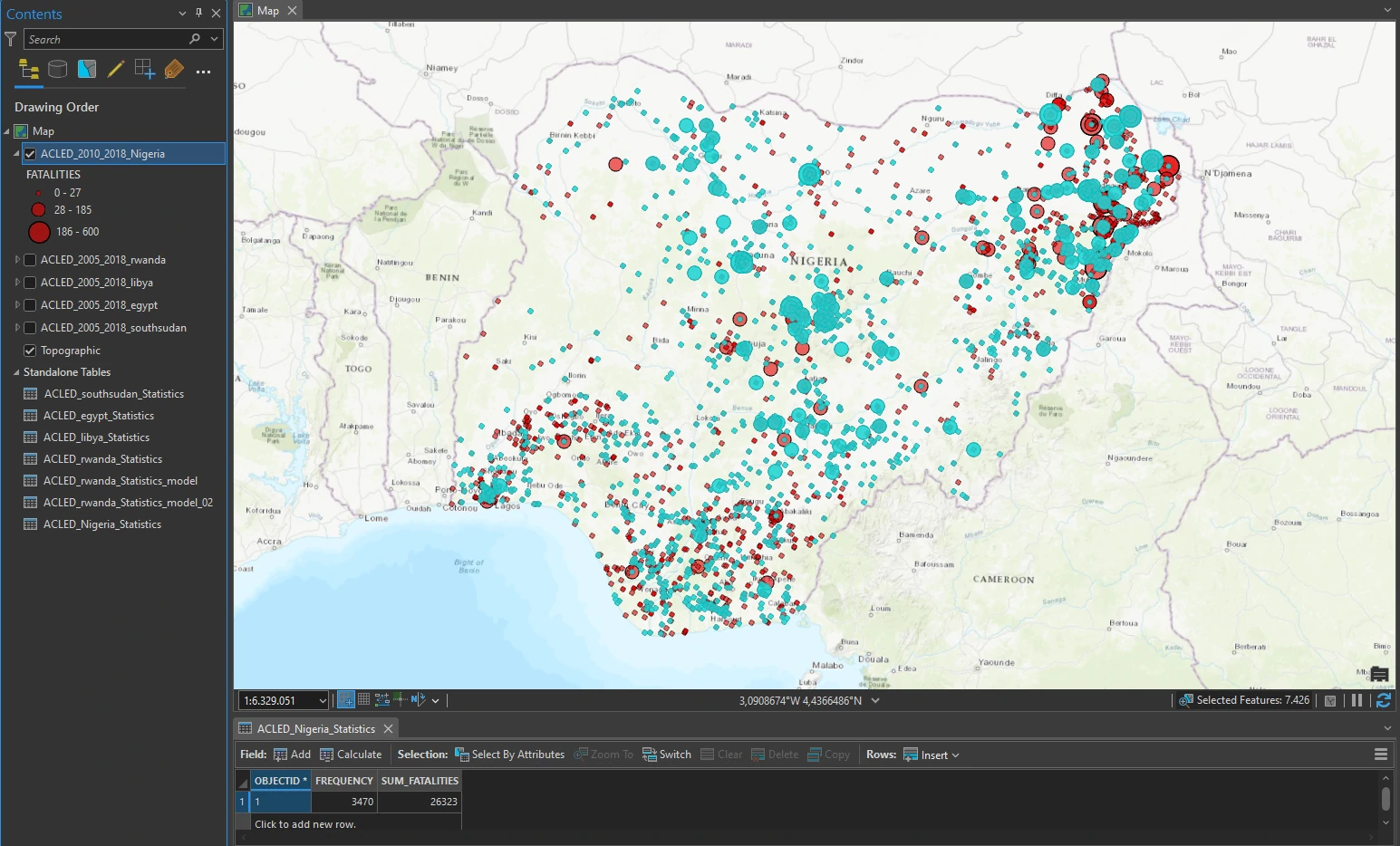
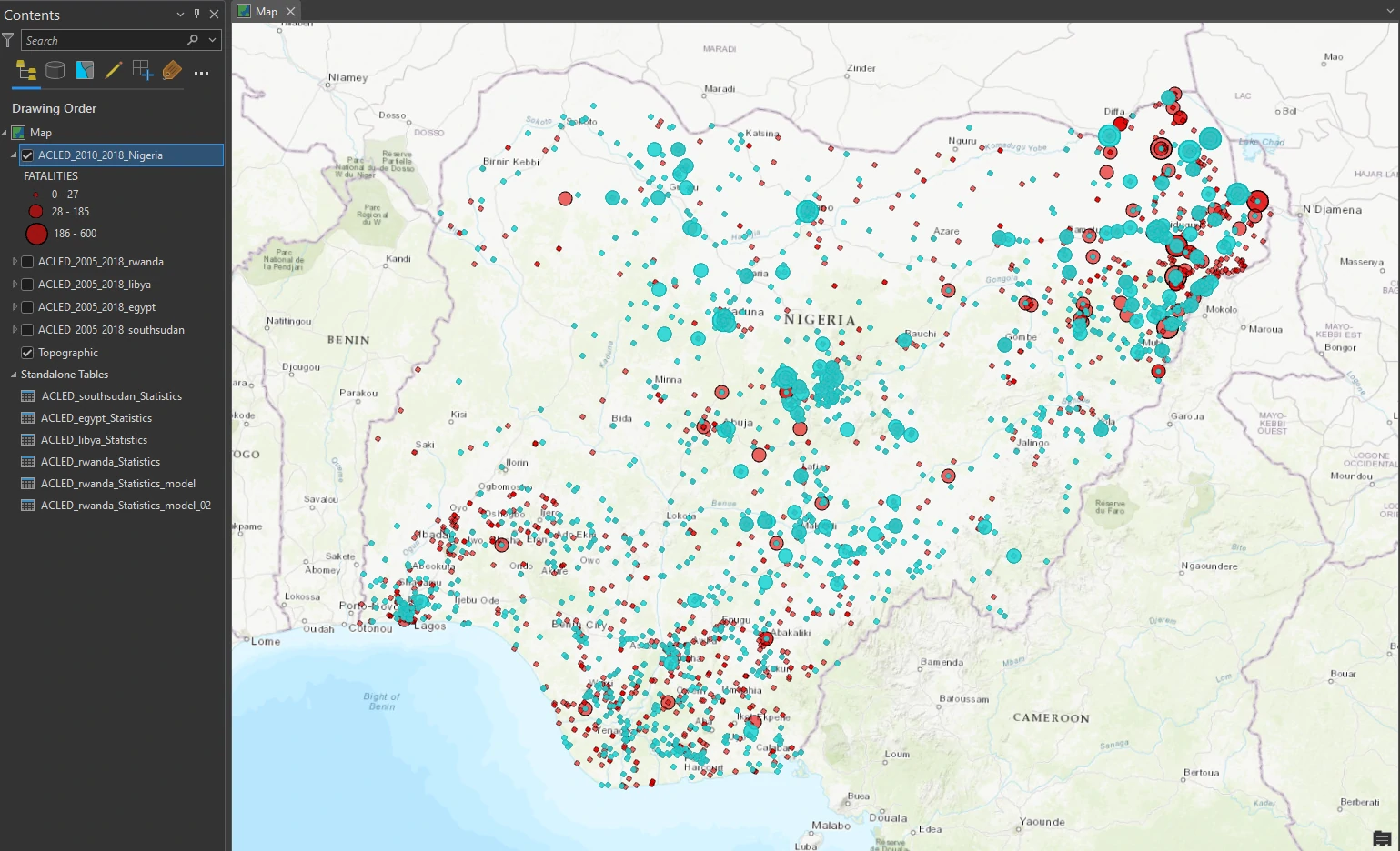
We will continue using our previous dataset. We filter the layer’s definition to the country of Nigeria, displaying conflicts between 2010 and 2018. Next, we will using graduated symbols based on the FATALITIES field. Use the default classification method, change the number of classes to 3.
Run a command using Python
Each process in ArcGIS Pro can be translate into Python script. In Example, we can translate Save to Layer File tool from Geoprocessing pane by right-click the status bar at the bottom of the Geoprocessing pane, and click Copy Python Command - Or we can alternatively copy the Python command from the geoprocessing history on the Analysis tab > Geoprocessing group. On the View menu, click the Python Window button. This process will copy python code for Save to Layer File tool into our clipboard.
To use python command and python code from tools, we can use - On the View menu, click the Python Window button, this step opens the Python window. Now we can paste our previous code from tool to this entry box.
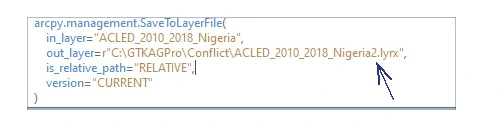
arcpy.management.SaveToLayerFile(
in_layer="ACLED_2010_2018_Nigeria",
out_layer=r"...\book\GTKAGPro\Conflict\ACLED_2010_2018_Nigeria_test_02.lyrx",
is_relative_path="RELATIVE",
version="CURRENT"
)
The process and parameters that we can input will be same as Save to Layer File tool.
This Python Window act as terminal python that we can input all python code in it. in example:
import arcpy # load the library
arcpy.env.workspace = 'C:/GTKAGPro/Conflict' # setup the workspace
Use a custom script tool
Script tools look like any ArcGIS geoprocessing tool, except that they are based on a Python script. We can use Python to create a custom geoprocessing tool. Similar to creating a geoprocessing tool based on a model, the tool author specifies the tool parameters that the end user can modify.
We can create script tool by right-click a toolbox in the Catalog pane and click New > Script. In example we can use this Select and Summarize custom script :
# Select and Summarize
------------------------------------------------------------------
# Created on: 2024-05-28
#
# Description: The user can select an input file to symbolize and an output file to store the summary results
------------------------------------------------------------------
# Import arcpy module
import arcpy
from arcpy import env
# Set the environment for output file location
env.workspace = ("c:\GTKAGPro\Conflict\Conflict.gdb")
# Prompt the user for the name of the input layer
ACLED_2005_2018_InputFile = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)
# Prompt the user for the name of the output file
ACLED_2010_2018_Output_Stats = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1)
# Process: Select Layer By Attribute
arcpy.SelectLayerByAttribute_management(ACLED_2005_2018_InputFile, "NEW_SELECTION", "EVENT_TYPE = 'Violence against civilians'", "")
# Process: Summary Statistics
arcpy.Statistics_analysis(ACLED_2005_2018_InputFile, ACLED_2010_2018_Output_Stats, "FATALITIES SUM", "")
The code includes the tool name, creation date, and description, followed by the processing instructions: the call to import ArcPy, environment settings, geoprocessing tool parameters, and the geoprocessing tools run by the script.
Next, we can run out custom script tool by in the Catalog pane, right-click the Select and Summarize script tool, and click Open.