Kedro 101
tools
simulation
Kedro

Introduction
Kedro is an open-source Python framework that helps data scientists and engineers build reliable, scalable, and maintainable data pipelines. It brings best practices from software engineering into data science projects, making it easier to move from exploration to production.
Why Use Kedro?
- Modularity & Reusability – Organizes code in a structured, reusable way.
- Pipeline Management – Helps design and visualize complex workflows.
- Configuration Management – Keeps secrets and parameters cleanly separated.
- Testing & Versioning – Encourages best practices like unit testing and reproducibility.
- Seamless Deployment – Works well with cloud platforms and production environments.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Kedro
-
Install Kedro
Make sure we have Python installed, then run:
pip install kedro -
Create a New Kedro Project
To create a new project, we can run
kedro new.kedro new --telemetry=noThere are some templates that we can used such as:
- Default spaceflights starter (
spaceflights-pandas): Added if we selected any combination of linting, testing, custom logging, documentation, and data structure, unless we also selected PySpark or Kedro Viz. - PySpark spaceflights starter (
spaceflights-pyspark): Added if we selected PySpark with any other tools, unless we also selected Kedro Viz. - Kedro Viz spaceflights starter (
spaceflights-pandas-viz): Added if Kedro Viz was one of our tools choices, unless we also selected PySpark. - Full feature spaceflights starter (
spaceflights-pyspark-viz): Added if we selected all available tools, including PySpark and Kedro Viz.
These templates can be used by:
kedro new --starter=spaceflights-pandas-viz --telemetry=noNext, we will be ask to type our project and folder name.
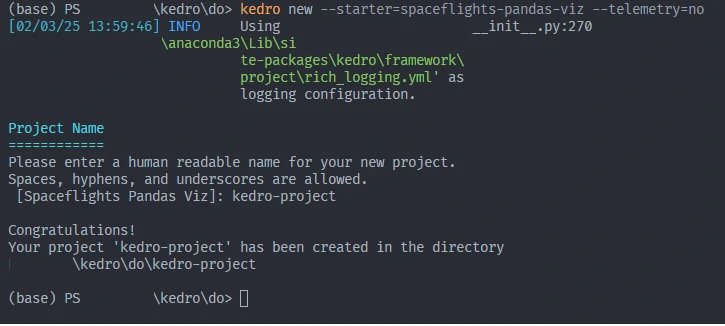
- Default spaceflights starter (
-
Install all Libraries at requirements.txt
pip install requirements.txt -
Understand the Project Structure
A typical Kedro project looks like this:
my_kedro_project/ ├── data/ # Data storage ├── conf/ # Configuration files ├── src/ # Source code │ ├── pipelines/ # pipelines │ ├── pipeline_registry.py # Dataset management │ ├── settings.py # setting └── tests/ # Unit tests -
Additionally, we can add notebook folder to store all jupyter notebook that used for the modeling
my_kedro_project/ ├── data/ # Data storage ├── conf/ # Configuration files ├── notebook/ # for jupyter notebook files ├── src/ # Source code │ ├── pipelines/ # pipelines │ ├── pipeline_registry.py # Dataset management │ ├── settings.py # setting └── tests/ # Unit tests -
Prepare our jupyter notebook to do data science things.
-
Convert all process into function to make it easier to implement into kedro
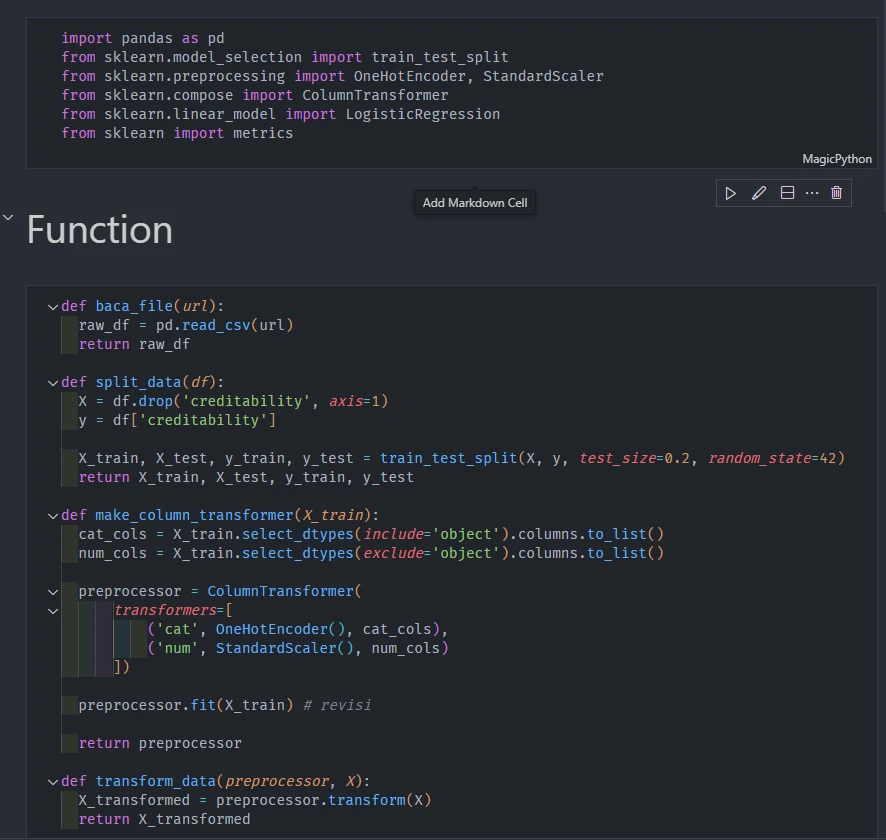
-
Build Our First Data Pipeline
Kedro uses nodes (functions) and pipelines (workflow sequences).
let’s say we have 2 process, that do a data engineering and modeling. We can split these process into 2 folders.
my_kedro_project/ ├── data/ # Data storage ├── conf/ # Configuration files ├── notebook/ # for jupyter notebook files ├── src/ # Source code │ ├── pipelines/ # Pipelines folder │ │ ├── data_preprocessing # Data processing pipelines │ │ │ ├── pipeline.py # Pipeline process for data preprocessing │ │ │ └── nodes.py # Data transformation functions │ │ └── modeling # Modeling pipelines │ │ │ ├── pipeline.py # Pipeline process for modeling │ │ │ └── nodes.py # Data transformation functions │ ├── pipeline_registry.py # Dataset management │ ├── settings.py # setting └ ...-
nodes.py
input all functions (and all library) at notebook in previous step into this file.
import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.preprocessing import OneHotEncoder, StandardScaler from sklearn.compose import ColumnTransformer def baca_file(url): raw_df = pd.read_csv(url) return raw_df ... -
pipeline.py
This file is a main process in kedro that run all registered Node in a Pipeline.
from kedro.pipeline import Pipeline, node, pipeline from .nodes import * def create_pipeline(**kwargs) -> Pipeline: return pipeline( [ node( func= baca_file, inputs='params:url', outputs='raw_df', name='baca_file' ) ] ) ...we can add all nodes inside
return pipelineline.
-
-
Define the Data Catalog
my_kedro_project/ ├── data/ # Data storage ├── conf/ # Configuration files │ └── base/ # base folder │ ├── parameters_data_preprocessing.yml │ ├── catalog.yml │ └── parameters_modeling.yml ├── notebook/ # for jupyter notebook files ├── src/ # Source code │ ├── pipelines/ # Pipelines folder │ │ ├── data_preprocessing # Data processing pipelines │ │ │ ├── pipeline.py # Pipeline process for data preprocessing │ │ │ └── nodes.py # Data transformation functions │ │ └── modeling # Modeling pipelines │ │ ├── pipeline.py # Pipeline process for modeling │ │ └── nodes.py # Data transformation functions │ ├── pipeline_registry.py # Dataset management │ ├── settings.py # setting └ ...We can define all input and output data that used by pipeline.
-
Define input data Create a file at
conf/base/parameters_data_preprocessing.ymlto specify where data comes from, let say that the data come from url. we can define it using:url: https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/e/ ... pub?gid=0&single=true&output=csvwe can also used
parameters_modeling.yamlif there are files that used in modeling process. -
Define output data Edit
conf/base/catalog.ymlto specify where data comes from:raw_data: type: pandas.CSVDataSet filepath: data/01_raw/raw_data.csv
cleaned_data: type: pandas.CSVDataSet filepath: data/02_intermediate/cleaned_data.csv
The results will be stored in each folder at filepath.
-
-
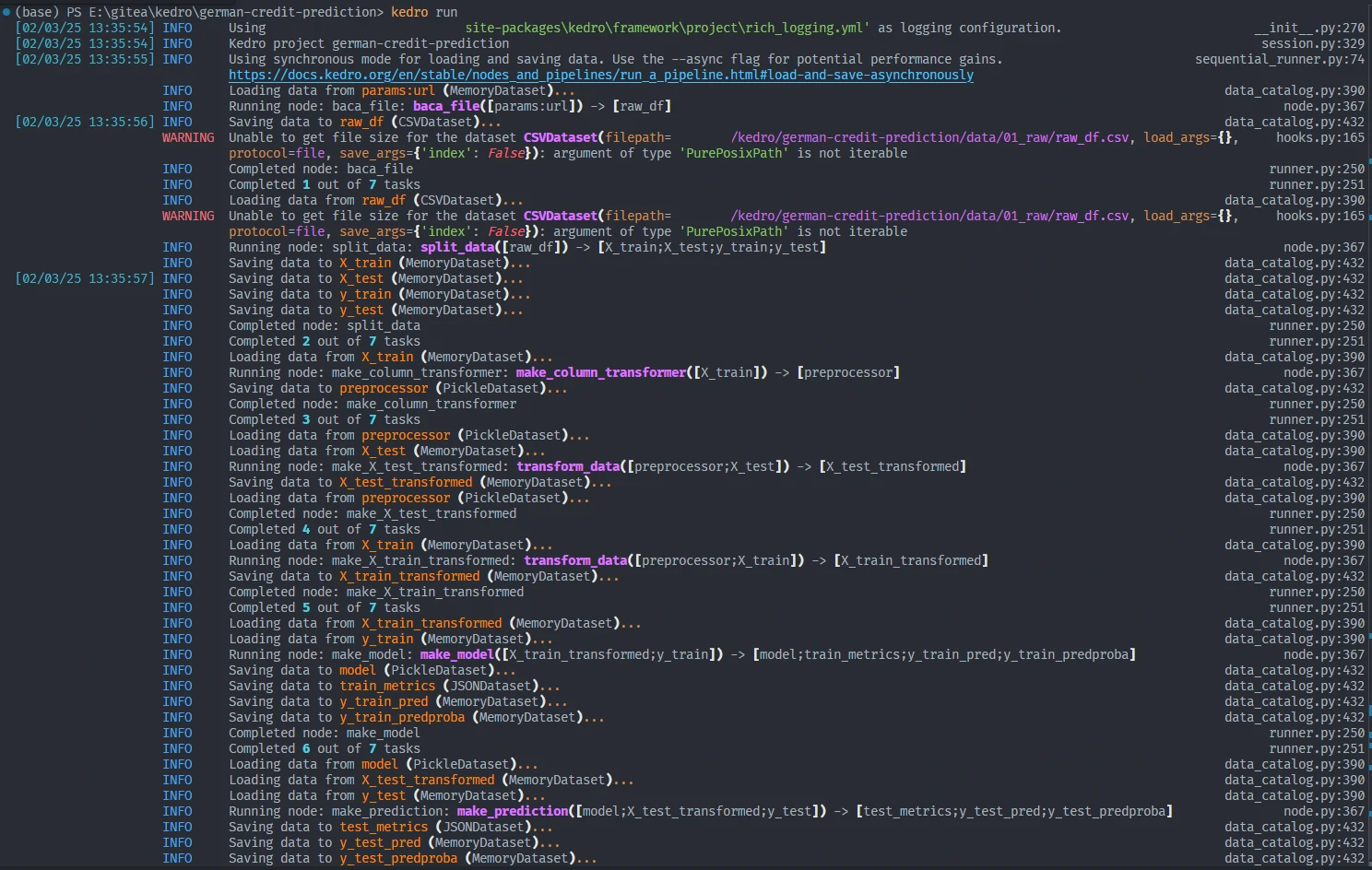
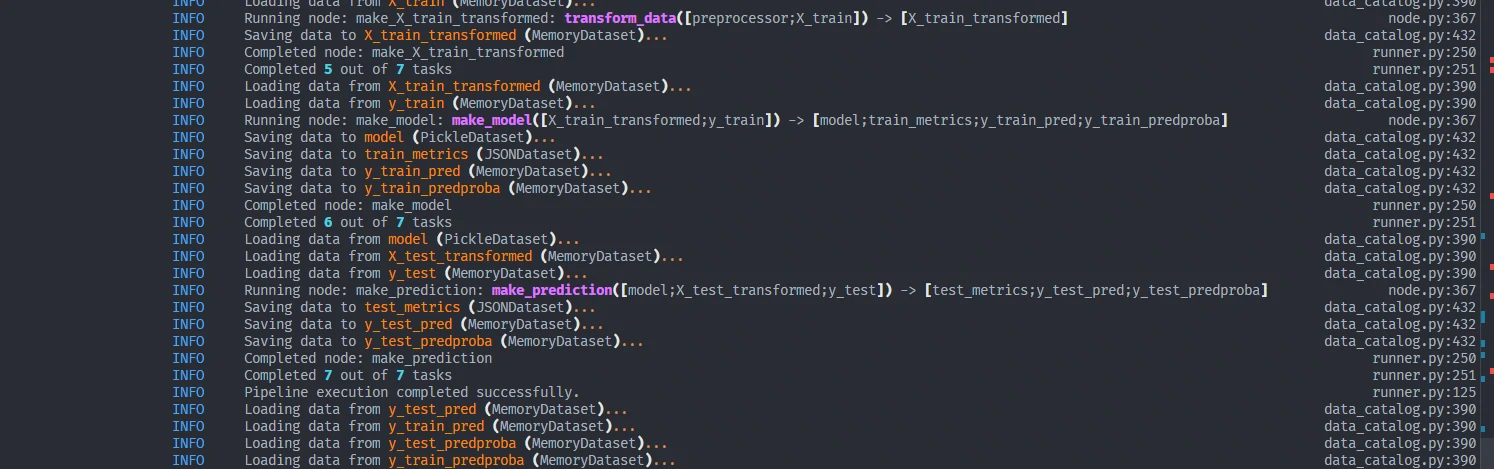
Run the Pipeline
kedro runKedro will automatically execute the pipeline and store the processed data in the specified locations.
-
Visualize the Pipeline
To see how your data flows through the pipeline:
kedro vizThis launches an interactive graph in your browser.
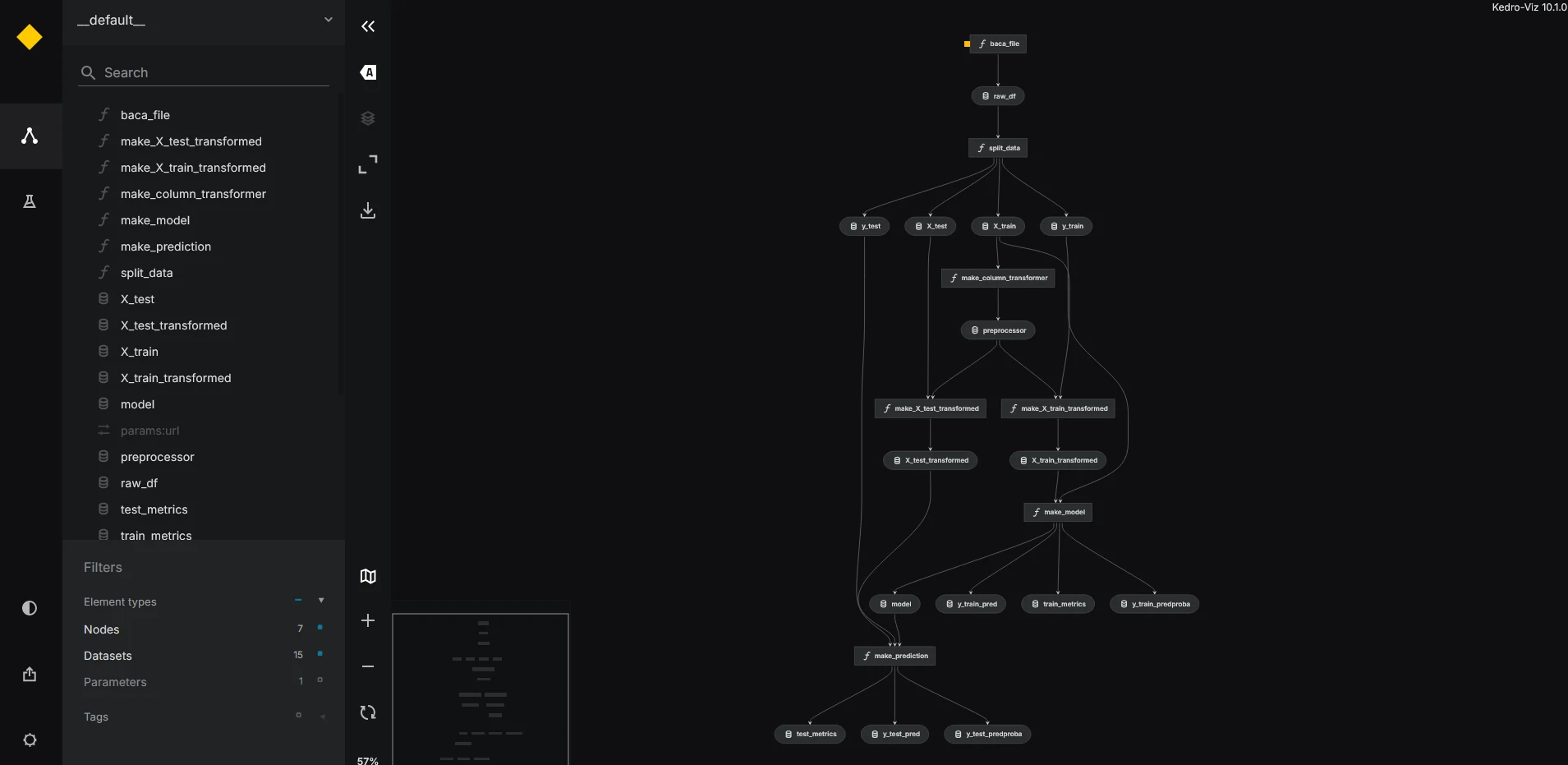
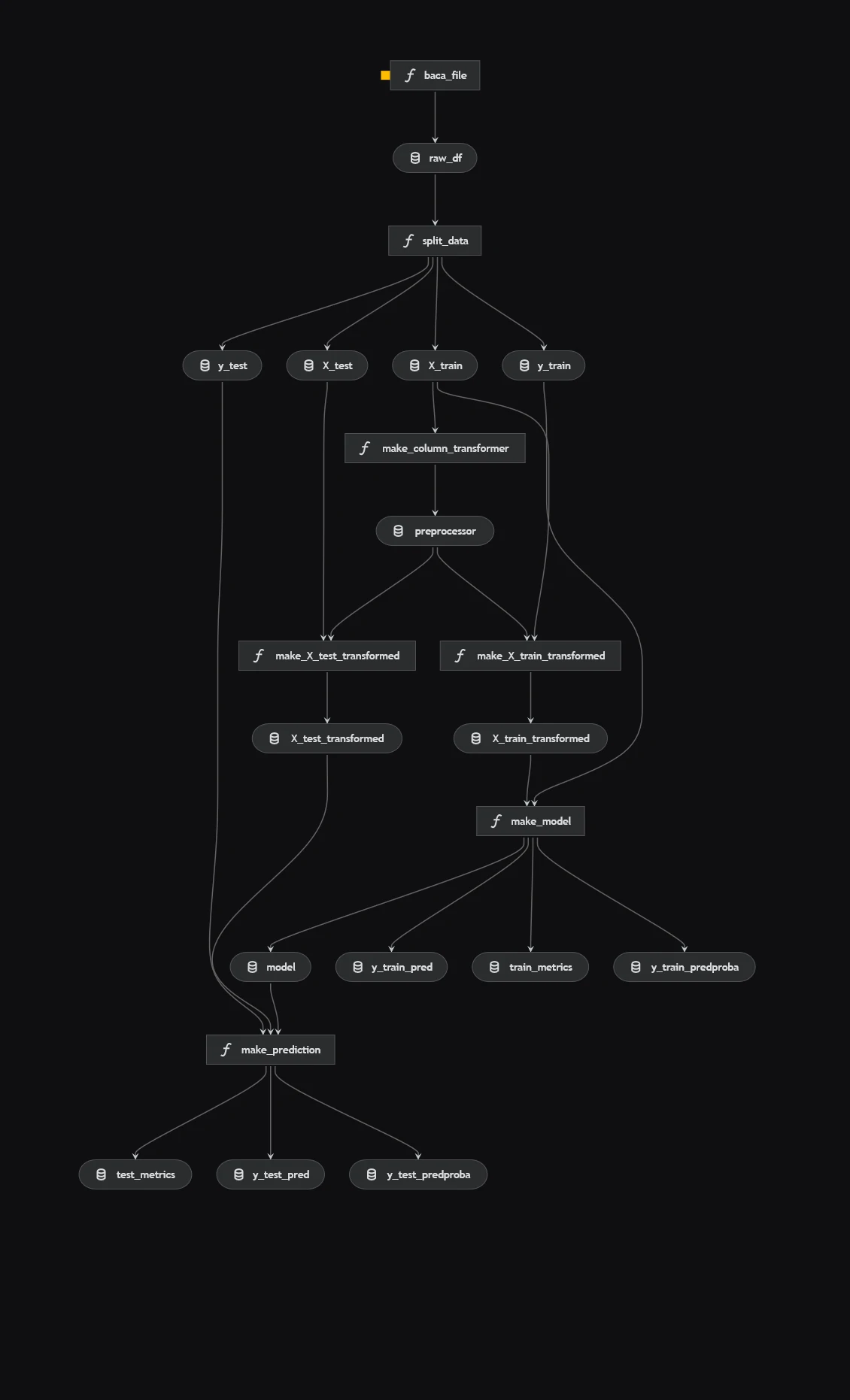
What’s Next?
Kedro is a powerful tool that can help you move from messy notebooks to well-structured, production-ready projects. Once comfortable, explore:
- Advanced Pipelines (Branching, Dependencies)
- Integrations with MLFlow, Airflow, and Cloud Services
- Custom Hooks & Plugins
Kedro makes data science cleaner, more efficient, and scalable.
reference
- https://docs.kedro.org/en/stable/index.html
- https://kedro.org/